之前团队存在的痛点
不同小组的接口协议差异化大,理解成本大。
不同服务是由不同开发去实现,如果需要流量控制或黑白名单逻辑,都需要自己重新实现,重复造轮子。
接口管理缺少线上的安全规范。
部分接口可能会缺少线上问题监控。
解决方案
自研(自定义功能)中台网关平台,后续新业务或迭代版本的接口都需要注册到网关进行统一管理。后续的硬性条件是接口接入网关后才允许线上的访问(后端服务的端口不开放公网环境,只能通过网关的内网请求进行通信)
平台元素
定时器,定时加载apollo配置,同步到redis
redis,提高配置读取速率
网关提供对外接口,接口注册、配置更新、服务下线、全局流量管理接口、健康检查、路由监控数据(暴露普罗米修斯格式指标)
apollo,网关路由管理的配置中心
网关的基本业务能力
路由管理、路由注册、路由发现、身份认证、负载均衡、流量控制、日志和监控、api缓存、接口代理
流量控制的测试点
流量控制的测试:
测试关注点:
约束条件-数值限制
testCase:
前置配置项 limit=10, time=10
模拟未命中约束条件场景,在9秒完成9次请求,期望值第十次请求时正常处理业务逻辑并返回正向结果。
模拟命中约束条件场景,在1秒内完成10次请求,期望值第十一次请求返回限流msg。
策略释放规则验证
测试模拟方法:
依赖python编写循环请求方法,在发起请求和结束请求后会打印上具体的时间,确保是在时间区间内完成的多次请求。
配置支持热更新
testCase:前置先准备路由A配置,在网关服务运行期间修改配置成B,等待配置生效,请求网关的代理接口,是否是遵循B配置执行
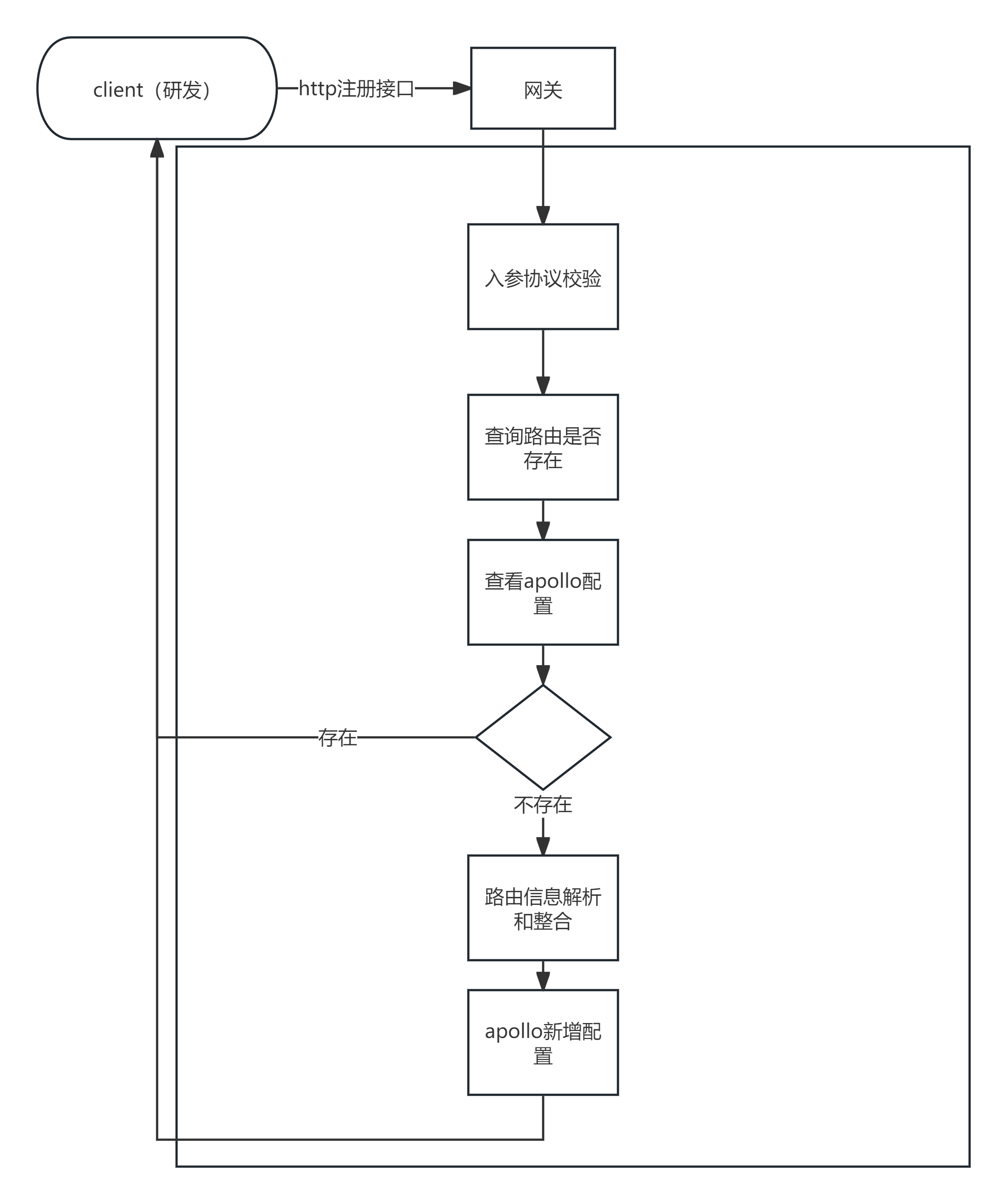
路由注册
schema = {
"type": "object", # 校验的外层是object结构
"properties": { # 定义每个字段的校验协议
"path": {"type": "string", "maxLength": 30},
"method": {"type": "array"},
"limitStatus": {"type": "boolean"},
"limitRequests": {"type": "integer"},
"limitTime": {"type": "integer"},
"hosts": {"type": "array"},
"jwtAuth": {"type": "boolean"},
},
"required": ["path", "method", "hosts"] # 定义必填项字段
}
@app.route('/route/register', methods=['post'])
def route_register():
# 入参协议校验
if not request.is_json:
return jsonify({'msg': 'data error'}), 403
try:
jsonschema.validate(instance=request.json, schema=schema) # instance->要校验的对象 schema->协议
except jsonschema.exceptions.ValidationError as err:
print(err)
return {'msg': 'data error'}, 400
re_body = request.json
# 签名校验
if 'Sign' not in dict(request.headers).keys():
return jsonify({'msg': 'sign error'}), 401
else:
if not aes_decry(key=config['signKey'], iv=config['signIv'], text=request.headers.get('Sign')):
return jsonify({'msg': 'sign error'}), 401
# 查询已注册的路由配置
api_gateway_config = apolloOpera.get_apollo_config()
if request.json['path'] in api_gateway_config.keys():
return jsonify({'msg': 'route already exist'}), 403
route_values = {
'method': request.json['method'],
"limitStatus": re_body.get('limitStatus') or False,
"limitRequests": re_body.get('limitRequests') or 0,
"limitTime": re_body.get('limitTime') or 0,
"hosts": re_body.get('hosts'),
"jwtAuth": re_body.get('jwtAuth') or False
}
# apollo配置新增
if apolloOpera.create_apollo_config(new_route=request.json['path'], route_value=json.dumps(route_values)):
return jsonify({'msg': 'route register success'}), 200
else:
return jsonify({'msg': 'route register fail'}), 403实现单接口全局流量控制
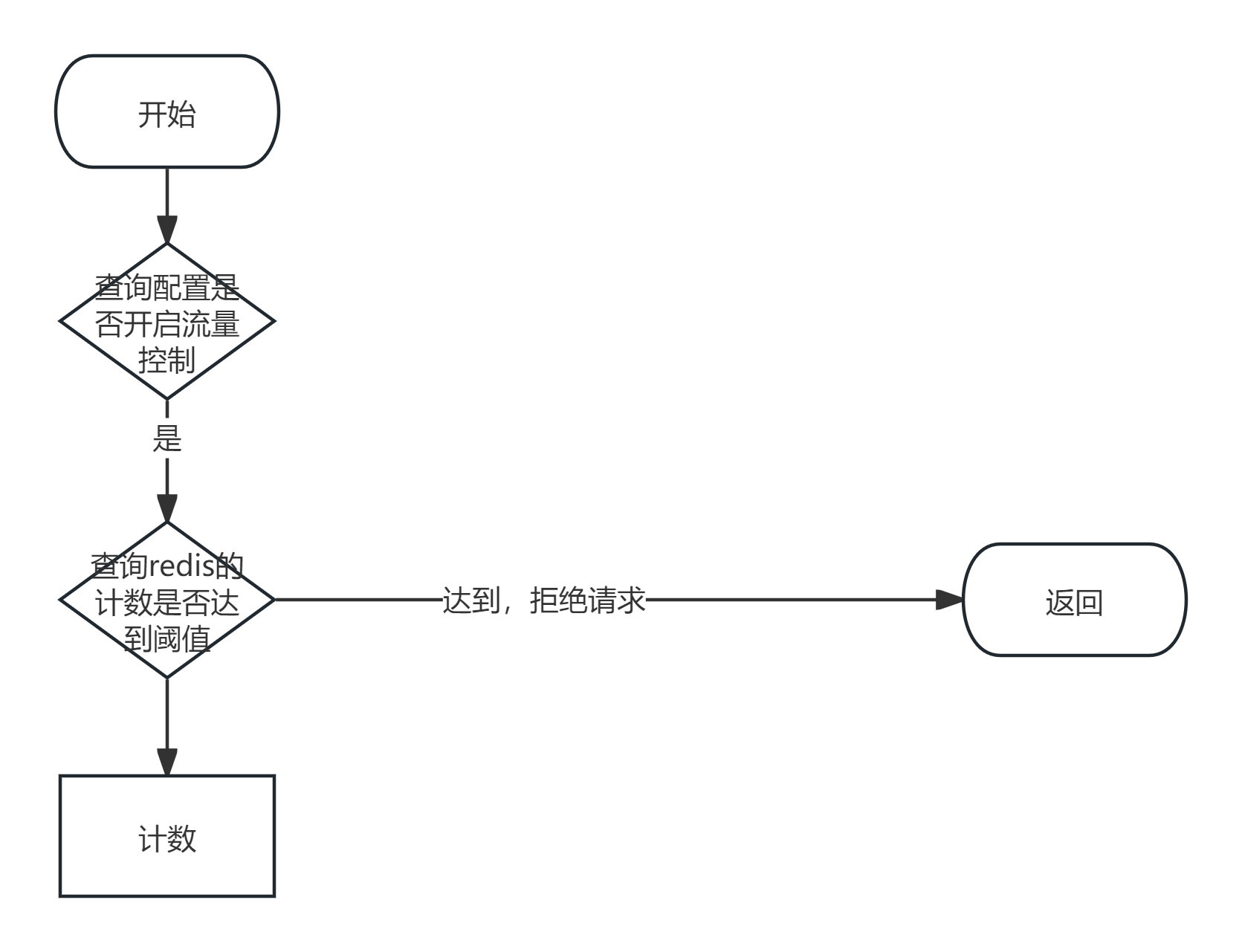
# 接口的流量控制
all_key = f'all_limit:{path}'
count = int(redis_conn.get(all_key) or 0)
if count > 10000:
return jsonify({'msg': 'server busy'}), 502
else:
count += 1
redis_conn.set(all_key, count, ex=60)负载均衡实现
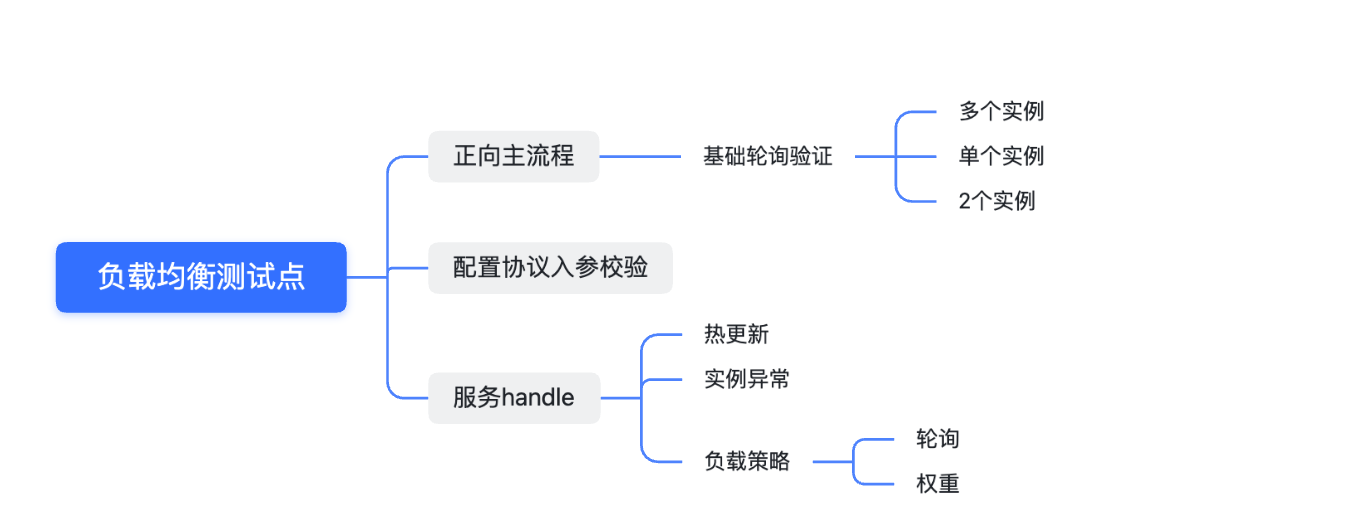
和nginx的覆盖均衡目的是一样,基于单接口维度转发到不同的服务实例。
负载均衡策略实现:
轮巡:需要实现轮巡实例的计算公式,同时需要依赖redis进行实例请求次数的计数。
权重分配:需要实现权重分配的计算公式,公式原理需要把所有权重加到一块再根据不同实例权重进行实例索引的切片,这里也需要基于redis进行实例请求次数计数,根据当前计数数值计算命中的切片区间,也就对应着负载的实例。
# 负载均衡(轮巡)
if len(route_config['hosts']) >= 2:
host_count_key = f'host_count:{path}'
count = int(redis_conn.get(host_count_key) or 0)
host_index = count % len(route_config['hosts'])
url = route_config['hosts'][host_index] + '/' + path
count += 1
redis_conn.set(host_count_key, count)
else:
url = route_config['hosts'][0] + '/' + path
负载均衡测试点